


Rendering complex chatbot responses, including mathematical equations, code snippets, and custom-styled text utilizing ReactMarkdown, RemarkMath, and rehypeKatex in a Remix application.
In an era where artificial intelligence and natural language processing are rapidly advancing, chatbots have evolved from simple question-answering tools to sophisticated conversational agents capable of discussing complex topics. As these AI-powered assistants tackle increasingly diverse and intricate subjects, the need for rich, formatted responses has become paramount.
Imagine a chatbot discussing advanced physics concepts, explaining intricate mathematical proofs, or providing code snippets for a programming tutorial. Traditional plain text responses fall short in these scenarios. Users need to see properly formatted equations and well-structured content to truly grasp the information being conveyed.
This is where the challenge of rendering complex responses comes into play. Modern chatbots require the ability to dynamically generate and display content with:
- Mathematical equations and symbols
- Formatted code snippets
- Rich text formatting (headings, lists, bold, italic, etc.)
- Custom styling to match the application's design
In this article, we'll explore a powerful custom Remix component that utilizes the capabilities of ReactMarkdown, RemarkMath, and rehypeKatex to address these challenges head-on.
Our focus will be on the CustomMarkdownRenderer component – a flexible and feature-rich solution that I designed to transform raw markdown and LaTeX input into beautifully formatted, interactive content. This component not only handles standard markdown syntax but also processes mathematical notations, automatically converts certain expressions to Unicode, and applies custom styling to enhance readability and user experience.
By the end of this deep dive, you'll understand:
- How ReactMarkdown serves as the foundation for rendering complex markdown content
- The role of RemarkMath in parsing mathematical notations within markdown
- How rehypeKatex brings LaTeX rendering capabilities to our component
- The intricacies of preprocessing content to handle various edge cases and improve rendering
- Techniques for customizing the rendering and styling of different markdown elements
So, let's get to it and start this journey to unlock the full potential of formatted chatbot responses and elevate the user experience in your React applications.
Component Overview
My CustomMarkdownRenderer is a Remix/React component designed to take Markdown content as input and render it with advanced formatting capabilities. Here are the key features:
- Markdown rendering with ReactMarkdown
- Mathematical equation support using RemarkMath and rehypeKatex
- Custom styling for various Markdown elements
- Unicode conversion for certain mathematical notations
Key Dependencies
The component relies on several important libraries:
ReactMarkdown:The core library for rendering Markdown content in Reactremark-math:A plugin for parsing mathematical notation in Markdownrehype-katex:A plugin for rendering mathematical notation using KaTeXKaTeX:A fast math typesetting library for the web
These features work in concert to ensure comprehensive coverage of various content types, with a particular emphasis on mathematical expressions. ReactMarkdown forms the foundation, handling standard Markdown syntax with ease. For mathematical content, we employ a two-pronged approach: RemarkMath and rehypeKatex tackle complex LaTeX equations, rendering them beautifully inline or as block elements, while our custom Unicode conversion functions handle simpler notations like superscripts and Greek letters.
This dual strategy ensures that whether a chatbot response includes a simple exponent or a complex integral, it's rendered accurately and legibly. The custom styling then steps in to ensure that all elements, from paragraphs to code blocks, are visually consistent and appealing. By layering these methods, we've created a robust system capable of handling the diverse range of content that modern AI-powered chatbots might generate, from simple formatted text to intricate mathematical proofs.
Preprocessing Content
One of the most interesting aspects of this component is its content preprocessing. The preprocessContent function performs several important tasks:
- Preserves LaTeX expressions for proper processing by rehype-katex
- Converts certain LaTeX-style math notations to inline math format
- Converts non-LaTeX math notations and exponents to Unicode characters
Let's look at the convertMathToUnicode function:
const convertMathToUnicode = (text: string): string => {
return text
.replace(/\frac{([^}]+)}{([^}]+)}/g, "($1)/($2)")
.replace(/\sqrt{([^}]+)}/g, "√($1)")
.replace(/\pm/g, "±")
.replace(/\^({[^}]+}|d+)/g, (_, p1) => {
// Convert exponents to Unicode superscripts
})
.replace(/\([a-zA-Z]+)/g, (match, p1) => {
// Convert Greek letter commands to Unicode
});
};This function handles various mathematical notations:
- Fractions are converted to a more readable inline format
- Square roots are replaced with the √ symbol
- The plus-minus symbol (±) is properly rendered
- Exponents are converted to Unicode superscripts
- Greek letters are replaced with their Unicode equivalents
Custom Rendering
The component uses ReactMarkdown's components prop to customize the rendering of various Markdown elements. For example:
components={{
p: ({ node, children }) => {
return <p className="custom-paragraph">{children}</p>;
},
h1: ({ node, ...props }) => (
<h1 className="custom-heading1" {...props} />
),
// ... other element customizations
}}This allows for fine-grained control over the styling and structure of the rendered Markdown.
Mathematical Equations
To handle mathematical equations, the component uses RemarkMath and rehypeKatex. The math prop in the CustomMarkdownRenderer component triggers the processing of LaTeX expressions:
const CustomMarkdownRenderer = ({ content }: { content: string }) => {
return (
<ReactMarkdown
components={components}
remarkPlugins={[remarkMath]}
rehypePlugins={[rehypeKatex]}
>
{preprocessContent(content)}
</ReactMarkdown>
);
};This setup ensures that mathematical expressions are correctly parsed and rendered using KaTeX.
Styling and Theming
The component's styling is handled through CSS classes and global styles. By applying custom classes to different Markdown elements, we can control their appearance and layout. For example:
.markdown-content {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
}
.custom-paragraph {
margin: 0.7vh 0;
}
.custom-heading1 {
font-size: 3vh;
padding-top: 2.5vh;
font-weight: semibold;
text-shadow: 0.1vh 0.1vh 0.2vh #000;
}
// ... other stylesThese styles use viewport height (vh) units for responsive sizing and include subtle effects like text shadows for headings.
See it in action!
Now that we've explored the inner workings of the CustomMarkdownRenderer component, you might be wondering how all these pieces come together in practice. Our component's power lies in its ability to seamlessly combine ReactMarkdown's flexibility, the mathematical precision of typesetting libraries, and our custom preprocessing logic. This synergy creates a robust solution capable of handling a wide range of formatting challenges, from simple text styling to complex equations and code snippets.
But as any developer knows, the proof is in the implementation. So, let's move from theory to practice and see this component in action! Below, you'll find the complete code for the CustomMarkdownRenderer, ready to be integrated into your React application. This example will demonstrate how our component transforms raw markdown input into beautifully formatted, interactive content.
npm i react-markdown
npm i rehype-katex
npm i remark-mathImage 1: Initial User Query
This image shows the initial interaction between a user (identified as "Teacher") and the chatbot named "Lumi". The teacher's request to plan a lesson on the quadratic formula immediately highlights the need for sophisticated mathematical rendering.
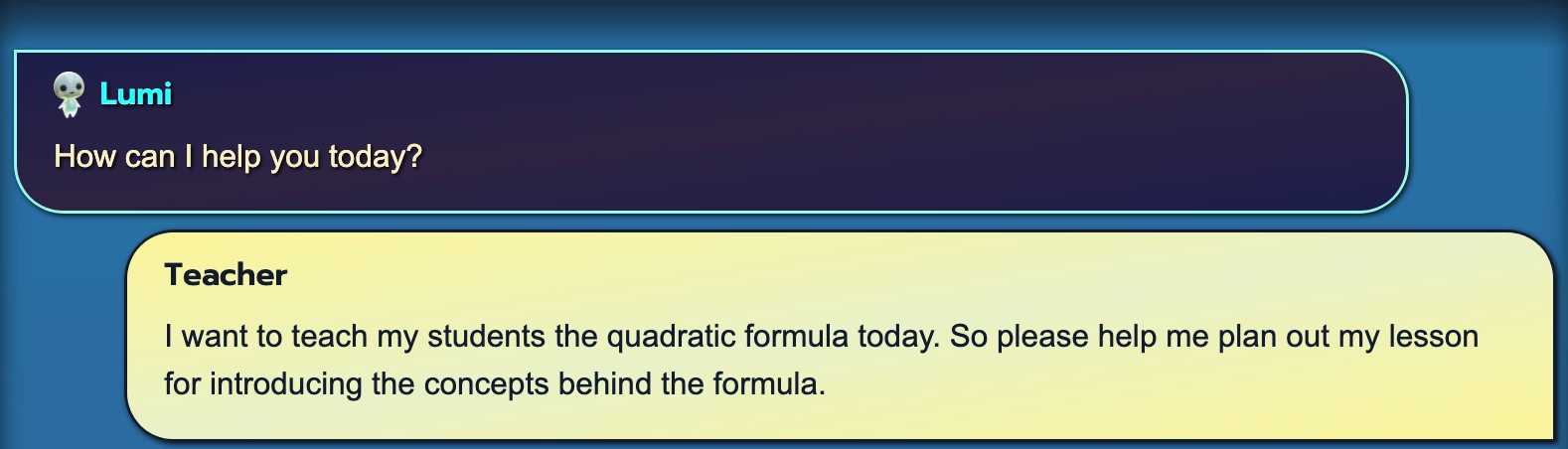
Image 2: Chatbot's Lesson Plan Response
In the following image, we see Lumi's detailed response to the teacher's request. The response showcases the chatbot's ability to generate structured, formatted content:
- It presents a well-organized "Lesson Plan" with clear headings and subheadings.
- The plan includes an objective, materials needed, and a lesson outline.
- Mathematical equations are rendered properly, demonstrating the component's ability to handle LaTeX or similar math notation (e.g., ax² + bx + c = 0).
This response illustrates how the custom markdown component can render complex, structured text with proper formatting and mathematical expressions.

Image 3: Continuation of the Lesson Plan
The CustomMarkdownRenderer component demonstrates its versatility and power in rendering complex mathematical and textual content in the following image. It seamlessly integrates different formatting styles, from basic text to intricate mathematical notation. The component renders section headers like "Deriving the Quadratic Formula" and "Working Examples" with distinct styling, likely using custom CSS classes for emphasis.
The quadratic formula itself is a standout feature, rendered as a complex mathematical expression with superscripts, fractions, and square roots, showcasing the component's ability to interpret and display LaTeX-style mathematical notation. The renderer maintains consistent formatting for bullet points and numbered lists, ensuring a clear hierarchical structure. It also handles inline mathematical expressions within regular text, as seen in the example equations (x² - 5x + 6 = 0) and (2x² + 4x - 6 = 0), where superscripts are correctly displayed.
This combination of features illustrates the CustomMarkdownRenderer's capability to transform raw markdown and LaTeX input into a visually appealing and mathematically accurate representation, essential for educational content in a chat interface.

Image 4: React Component for Quadratic Formula Calculator
Our next example demonstrates the CustomMarkdownRenderer's advanced capabilities in presenting both explanatory text and code snippets within a chat interface, specifically in an educational context about the quadratic formula:
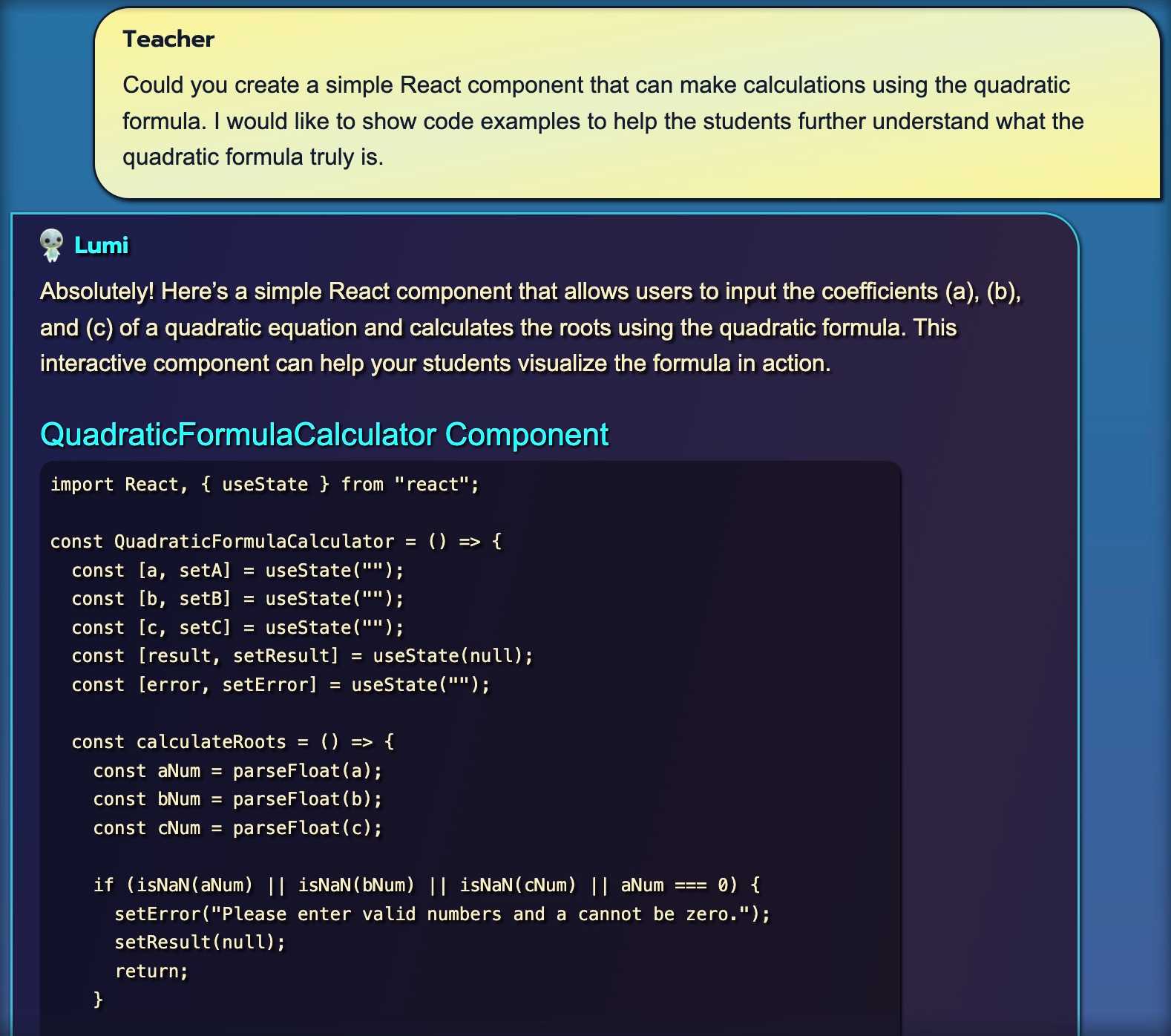
Chat Interface
- The image maintains the consistent chat bubble design, with distinct styles for the user (Teacher) and the AI assistant (Lumi).
- This continuity in design helps users follow the conversation flow easily, even when complex content is introduced.
Text Rendering
- The component renders regular text with appropriate formatting, including different font weights for emphasis.
- Lumi's response is well-structured, with a clear introduction and explanation of the upcoming code.
Code Block Presentation
- The code is displayed in a distinct, dark-themed block, setting it apart from the regular text.
Typography and Readability
- The code uses a monospaced font, typical for coding, which aids in readability and code alignment.
- The contrast between the dark code background and light text ensures good legibility.
This example showcases how the CustomMarkdownRenderer can seamlessly integrate complex, formatted text with syntax-highlighted code snippets, making it an invaluable tool for educational chatbots or any application requiring the presentation of technical content in a conversational interface.
Wrapping Up
The ability to present such diverse content types within a chat interface opens up new possibilities for educational platforms, technical support systems, and any application where complex information needs to be communicated clearly and effectively.
As AI continues to advance, tools like the CustomMarkdownRenderer will become increasingly crucial in bridging the gap between machine-generated content and human understanding. By enabling chatbots to communicate with the same depth and clarity as human experts, we're not just improving user interfaces – we're enhancing the very nature of human-AI interaction.
As we look to the future, we can anticipate even more advanced rendering capabilities, perhaps incorporating interactive elements or real-time data visualizations. The journey to perfect human-AI communication is ongoing, and components like the CustomMarkdownRenderer are pivotal in this evolution.
By using such customization as we have explored today, you're not just improving your application's functionality – you're contributing to a future where complex ideas can be shared effortlessly between humans and AI, fostering better understanding and more productive interactions.